Cost and adaptability are pivotal for widespread welding innovation adoption
November 1, 2023 12:48 pm
Highlighting technology and productivity evolving the welding industry, Nimesh Chinoy, Director of Sales & Marketing SigmaWeld, explains how advancements in welding technology, automation, and training are reshaping the industry as we explore innovations, sustainability, and the skills needed for a brighter future.
How are advancements in welding technologies impacting productivity in the manufacturing industry?
Productivity and data analysis are the key drivers for welding technologies behind the transformative impact of welding technologies on the manufacturing industry.
Achieving a “first-time-right” outcome in welding becomes achievable when the appropriate parameters are employed according to the Welding Procedure Specification (WPS). A novel trend in welding equipment involves the capability to retrieve WPS data from a server, recognise the welder, and automatically configure the equipment to operate within the specified current and voltage range.
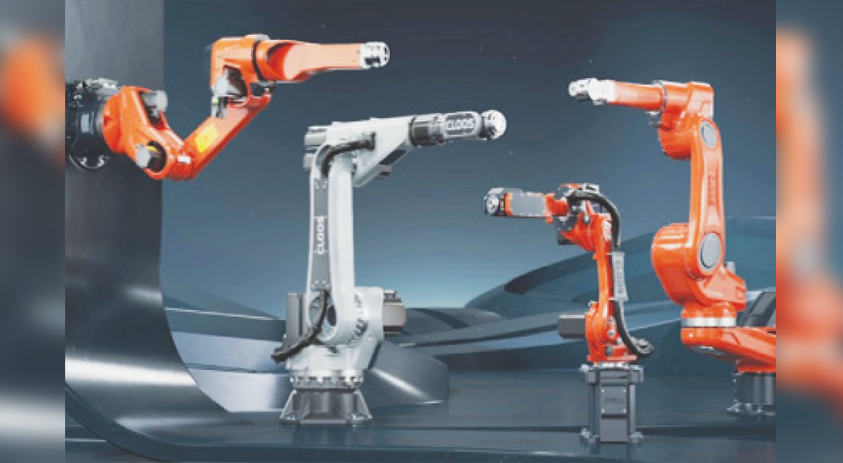
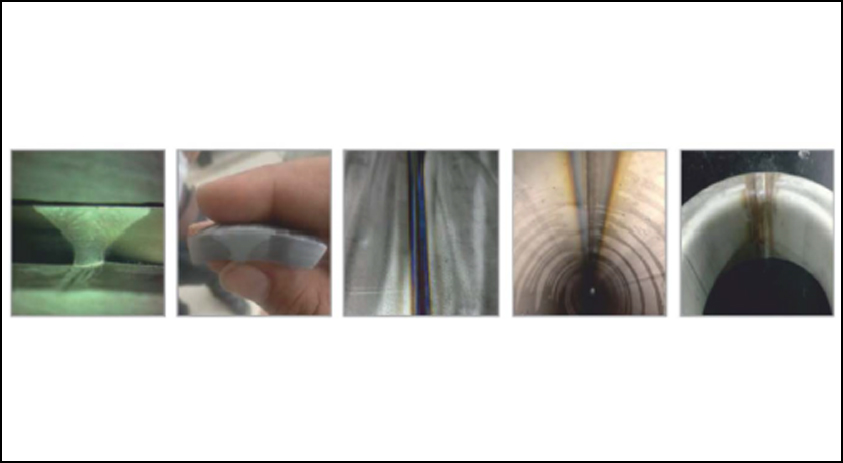
There is a growing emphasis on faster TIG processes like Keyhole Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), often referred to as SWAT, and advancements in more productive Submerged Arc Welding (SAW) techniques. The manufacturing industry is increasingly turning to automation, robots, and collaborative robots (cobots) due to the shortage of skilled workforce.
Additionally, handheld laser welding is gaining popularity for low-thickness materials.
How are advanced welding materials and techniques, including the SWAT method and automation, revolutionising the welding industry?
Contemporary welding relies heavily on advanced materials and techniques, serving as the bedrock of innovation. Specialised welding techniques are essential to accommodate high-strength alloys, exotic metals, and composite materials, ensuring the durability and long-term performance of welded structures. The SWAT technique, known for its unmatched precision, is crucial when working on intricate components. These approaches, when combined with automation and robotics, boost efficiency and also minimise the risk of errors. We leverage the potential of these advanced materials and techniques to ensure that our clients reap the full benefits of state-of-the-art welding technology, delivering robust, dependable, and high-performance results.
How do innovative technologies like SWAT welding contribute to a more sustainable and efficient future in the welding industry?
Our team is committed to ongoing exploration of innovative approaches aimed at reducing emissions and minimising energy consumption. Our SigmaWeld Induction Heaters are purpose-built for Pre Weld, Post Weld, and PWHT applications, effectively replacing conventional gas burner systems while achieving remarkable energy savings of up to 40% compared to resistance heating. This induction-based process is not only environmentally friendly but also incredibly energy-efficient, generating heat through the induction of eddy currents within the material, making it the most efficient preheating method.
In GTAW welding, the time-consuming need for edge preparation results in material waste. However, with SWAT technology, we can weld materials up to 12 mm thick without edge preparation, completing the welding in a single pass. This translates to a 90 percent reduction in the required passes, an 89 percent decrease in consumables for welding, a 77 percent reduction in gas usage, and nearly 100 percent less time spent on edge preparation.
Through our commitment to continuous improvement and responsible decision-making, we meet industry standards and surpass them, contributing to a greener and sustainable future.
How is SigmaWeld’s integration of IoT and data-driven technology into welding systems revolutionising the industry?
In the age of Industry 4.0, we take the lead in seamlessly merging welding technology with digitalisation and data-driven procedures. Our intelligent welding systems, equipped with sensors and IoT connectivity, collect real-time data for analysis. This data is processed using AI algorithms, enabling predictive maintenance to reduce downtime and enhance overall operational efficiency. Remote monitoring capabilities ensure swift responses to functional variations, guaranteeing uninterrupted production.
Recently, SigmaWeld has developed a range of welding machines that connect to the server through GPS/LAN/WIFI. The welding supervisor can configure parameters and assign WPS to the welder through the server software. When the welder logs attendance with their card, the parameters are transferred to the card. Subsequently, at the designated welding location, the welder scans their card on the welding machine, and the parameters are loaded onto the equipment. The welder can only adjust within the specified WPS range the supervisor sets. During welding, real-time data, including current, voltage, arcing time, welder details, and various other parameters, is logged and transmitted to the server. Remarkably, a single server software can connect to over 40 pieces of equipment.
How is strategic implementation of automation reshaping the welding industry to improve productivity?
We bring about a revolution in welding processes by strategically implementing automation, which enhances both productivity and the quality of the end product. Our automated welding systems are intricately designed to optimise operations, reducing manual errors and ensuring consistent, high-quality welds. Through the automation of repetitive tasks, we significantly increase production efficiency, allowing for faster turnaround times without compromising precision.
Our primary focus is on GTAW, known as one of the most critical and widely used processes in the industry, even though it’s considered slower. With years of experience and the development of AVC, Weavers, and Cold Wire Feeders, we can support various welding automation needs for this process. Our standard auto-tig heads can be easily integrated into existing automation equipment, such as seamers and column booms. This accelerates project delivery, and it also guarantees uniformity, meeting the most stringent quality standards.
To reiterate, the SWAT technique, a keyhole variant of GTAW, is the industry’s workhorse, significantly accelerating TIG welding, making it ten times faster than traditional methods. This approach is exceptionally cost-effective for welding stainless steel and exotic materials. One of our customers completed more than 4500 meters of welding 6mm of C276 nickel alloy without using a single consumable at speeds upwards of 400mm/min. This had a profound positive impact on their bottom line, saving them several months in production time.
How is the increasing demand for skilled welders in the manufacturing sector being addressed through automation and training programs?
The demand for skilled welders is steadily growing globally, particularly as the manufacturing sector thrives. With automation plays a significant role; it serves as a means to elevate the skills of welders to become operators. Nevertheless, having a solid foundation in welding knowledge remains a prerequisite for operating automation.
While automation handles repetitive tasks, there is a growing need in the industry for highly skilled welders who can proficiently manage complex machinery and ensure optimal performance. Training programs have adapted to this demand, focusing on advanced welding technologies, robotics, and programming. We acknowledge the critical role of a skilled workforce in this digital age. Our training initiatives are thoughtfully designed to guide welders in acquiring and staying current with the latest trends in the field, empowering them with the expertise necessary to operate advanced equipment effectively.
What transformations in productivity can we expect in the welding industry due to technological advancements, and what opportunities lie ahead for the future?
Achieving greater productivity with fewer resources is the goal, and we are seeing advancements in technologies like Friction Stir Welding, Key Hole Tig, and Plasma Welding that are driving these improvements. An intriguing development on the horizon is the use of travelling vacuum (localised) electron beam welding, which has the potential to enhance productivity significantly. However, cost and adaptability will be pivotal in its widespread adoption. The industry also moves toward more hybrid processes, leading to further innovations.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.


















 English
English Hindi
Hindi