An automation shift towards innovation and collaboration
July 11, 2023 6:46 pm
There has been a significant shift in the manufacturing sector with the widespread adoption of industrial automation. This transformation has revolutionised how production processes are carried out, resulting in unprecedented levels of productivity.
With the rapid advancements in technology, particularly in artificial intelligence (AI), industrial automation is poised to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of various industries. This analysis will explore the current industrial automation trends and their potential for future growth. Additionally, we will highlight its benefits while considering the challenges that may arise along the way.
Future growth potential
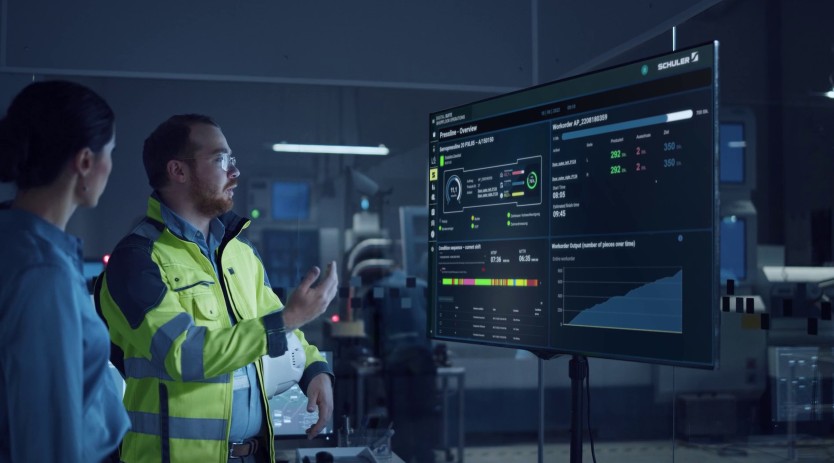
Integration of AI and Machine Learning: Integrating AI and machine learning algorithms is a prominent trend in industrial automation. These advanced technologies empower machines to learn from data, optimise operations, and autonomously make informed decisions.
Through the analysis of extensive real-time data, AI-driven systems can recognise patterns, identify anomalies, and enhance overall efficiency. This trend is expected to persist, with AI and machine learning becoming essential components of industrial automation, ultimately developing intelligent and adaptable manufacturing systems.
Collaborative Robotics: Cobots, or collaborative robots, have emerged as a popular choice for working alongside humans in a shared workspace. These robots are equipped with sensors and safety features that enable them to collaborate safely and effectively with human workers. Their popularity stems from their flexibility, user-friendly programming, and capacity to handle repetitive tasks. As robotics technology advances, we can anticipate a growing trend of humans and robots collaborating more closely, resulting in heightened productivity, enhanced ergonomics, and decreased operational expenses.
Industrial Internet of Things: IIoT encompasses a network of interconnected devices, sensors, and machines that gather and exchange data within an industrial environment. This interconnectedness facilitates smooth communication and data sharing among different elements of a manufacturing system, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and process optimisation. As the quantity of connected devices grows and the prevalence of 5G networks expands, IIoT will assume a crucial role as the foundation of industrial automation. This will improve efficiency, heightened productivity, and cost savings across various industries.
Edge computing: Edge computing involves the processing and analysis of data at or close to the location where it is generated, as opposed to transmitting it to a central cloud server. This methodology minimises delays, decreases bandwidth needs, and improves the ability to make real-time decisions. In the context of industrial automation, edge computing facilitates swift data analysis and response, enabling faster and more accurate control over machinery and processes. As edge computing devices become more prevalent and edge AI expands, this trend will significantly impact the development of intelligent and decentralised automation systems.
Cybersecurity and data protection: With the increasing interconnectivity and reliance on digital systems in industrial automation, it is vital to prioritise robust cybersecurity measures. Protecting sensitive data, preventing unauthorised access, and defending against cyber threats are essential for ensuring uninterrupted operations. In the future, industrial automation systems will emphasise implementing strong cybersecurity protocols, such as encryption, authentication, and secure communication channels, to mitigate risks and prevent potential breaches effectively.
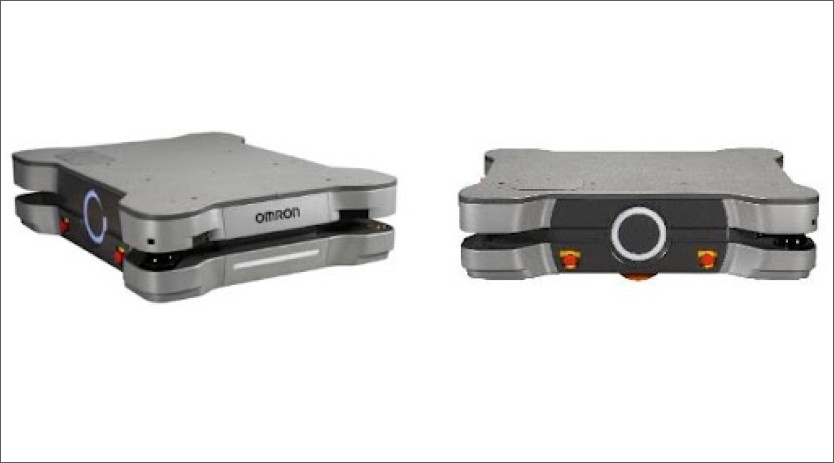
Autonomous mobile robots: AMRs are on the verge of revolutionising material handling and logistics processes in industrial environments. These robots are equipped with state-of-the-art sensors, mapping capabilities, and navigational algorithms, enabling them to navigate dynamic surroundings autonomously-AMRs efficiently transport materials, goods, and components, reducing manual labour and optimising supply chain operations. As AMR technology advances, we anticipate enhanced agility, adaptability, and collaboration between humans and robots in industrial settings.
Augmented reality for maintenance and training: Augmented Reality (AR) holds immense potential for transforming maintenance and training procedures in industrial automation. By superimposing digital information onto the physical environment, AR enables real-time guidance, instructions, and visualisations for technicians and operators. Through AR technology, remote troubleshooting, step-by-step assistance, and virtual simulations become feasible, resulting in minimised downtime, enhanced maintenance efficiency, and improved worker training. As AR applications advance in sophistication, they will empower industrial workers with valuable insights and assistance, ultimately boosting overall productivity and reducing errors.
Sustainable automation practices: Sustainability is rapidly gaining importance in industrial automation. Incorporating renewable energy sources, energy-efficient equipment, and optimised resource utilisation is driving the development of greener and more sustainable manufacturing practices. Automation is pivotal in enabling precise control over energy consumption, waste reduction, and the overall carbon footprint. As companies increasingly prioritise sustainability, we can anticipate the emergence of innovative eco-friendly automation technologies, including energy-efficient machinery, smart grids, and closed-loop systems. These advancements will significantly contribute to shaping a sustainable future.
Conclusion
The future of industrial automation is brimming with potential, fuelled by advancements in AI, robotics, IoT, AR, and sustainability initiatives. These forthcoming innovations will enhance operational efficiency and open doors to new business models, customisation options, and collaborations between humans and machines. As industries embrace these breakthroughs, we expect heightened productivity, cost savings, and a more sustainable and technologically advanced industrial landscape. The path toward the future of industrial automation is laden with opportunities, and transformative change is on the horizon.
Source – Balaji Switchgears Pvt. Ltd.
Email ID – Mktgindia@balajiswitchgears.com
Website – www.balajiswitchgears.com
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.

















 English
English Hindi
Hindi