Die and mould industry reshaping manufacturing innovations
September 30, 2023 12:57 pm
In a rapidly evolving landscape, the manufacturing sector faces unprecedented disruptions. Tools, a cornerstone of production, must adapt to varying sector needs. The Indian Die & Mold sector is primed for substantial growth, projected to surge by 10-15 percent in the coming years, as per TAGMA’s survey.
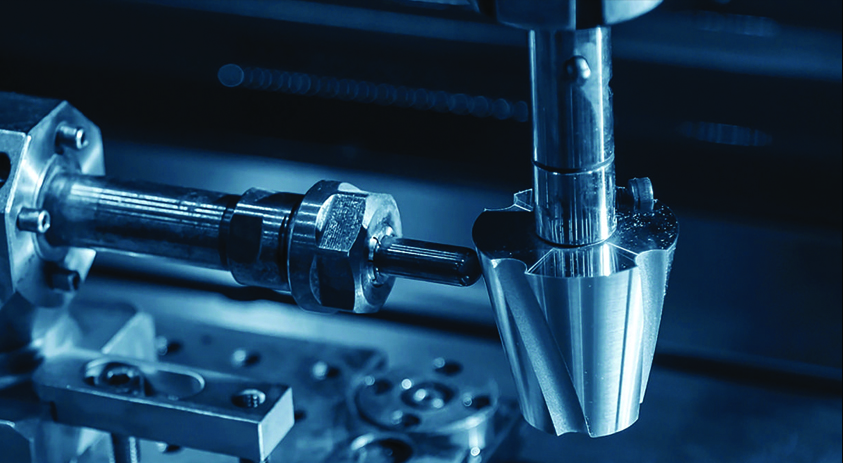
The die and mould industry is under a significant transformation. The manufacturers are embracing advanced manufacturing techniques. They are incorporating cutting-edge software solutions to optimise their machining processes, enhance efficiency, and achieve greater precision. Recently, with the rapid emergence of EVs, the development of autonomous cars is also happening faster, more than enough to propel innovation.
Vineet Seth, Managing Director of Mastercam APAC for South Asia and the Middle East, highlighted how the burgeoning EV industry had catalysed innovations within the die and mould sector. Manufacturers need to customise moulds explicitly tailored to the components required for EVs, such as battery casings and motor parts. Here, it is essential to prioritise the development of materials tailored for EV components. However, the particular emphasis has to be on factors such as efficient heat dissipation and weight reduction. The developments underscore the die and mould industry’s adaptability. It needs time to meet the distinctive demands of the expanding EV sector.
Consequently, the industry has to deliver tools more efficiently, with higher accuracy, and bracing for automation. That calls to incorporate automation. The innovative laser-cutting equipment is an example of automation in action, requiring less human intervention. Maulik Patel, Executive Director of Sahajanand Laser Technology, talked about the modern features of today’s laser cutting machines. These are compact and faster for more precise cutting speeds. He stated that these powerful machines should meet the features to cut various materials, including thin and thick metals such as steel and aluminium.
Technologies shaping the future
The emergence of 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, marks a departure from traditional subtractive methods. While subtractive manufacturing involves starting with a solid block and removing material until the desired part is achieved, 3D printing operates in reverse. In mould manufacturing, where injection, processing, cooling, and ejection are critical stages, efficient cooling is particularly vital. Shatyabrata Das, Senior General Manager at IAC-International Automotive Components, hints at the advantages of 3D printing in this context. With 3D printing, cooling channels can be designed and printed precisely to meet specifications, greatly enhancing cooling efficiency. This leads to faster cooling of moulded parts, ultimately reducing cycle times, a game-changer in manufacturing.
Further, CAD and CAM technologies are at the forefront of shaping the future of die and mould manufacturing. These two form the very foundation of this industry. One of the critical phases is mould design. Precision machines like CNC or VMC are employed in shaping the final product and bringing intricate designs to life. Now, the advanced 5X machines have emerged, representing the cutting edge of this technology. CAM involves translating the CAD model into machine-readable code, which the computer-controlled machinery comprehends and executes. In contemporary manufacturing, this CAD-to-CAM workflow has become indispensable. It now forms an integral part of the entire production process.
Discussing this transformative phase, Vineet emphasises how CAD and CAM technologies fundamentally reshape the die and mould manufacturing landscape in multiple ways. CAD empowers the creation of intricate and innovative mould and die designs with unparalleled precision. Moreover, introducing robotic systems capable of continuous operation round the clock plays a pivotal role in minimising downtime, thus enhancing production capacity.
Trends in the die and mould industry
The recent trends and technological advancements stand to reshape the way businesses operate, particularly in India. The localisation of mould production in India reduces development times, accelerating the overall product development process. One can be the integration of robots into the die and mould industry. Robots are pivotal in manufacturing plastic components, particularly when combined with dies and moulds.
The adoption of robotic systems interfacing with manufacturing machines is revolutionising production. This innovation has mitigated the risk of problems during the moulding process. As a result, robots in the moulding industry are propelling the sector’s growth and competitiveness.
Injection moulding is reshaping the way for the production of various plastic components. The mould manufacturers must adapt to meet the escalating demand for moulds that produce various injection-molded items. Even in delicate configurations, the plastic’s inherent moldability underscores the importance of precision machining and surface finishing processes in plastic injection moulding. Vineet emphasises the critical role of precision in this process. Injection moulding is of special use in the automotive industry for its plastic components.
One innovation that has made waves in injection moulding is ‘conformal cooling’. Leveraging the capabilities of 3D printing technology, conformal cooling has ushered in significant improvements in mould performance. Furthermore, smart software also is emerging as a game-changer in the metal forming industry.
Improvements and advancements
There have been advancements in providing more precise visualisations of multi-tasking machining processes. An aspect of CAM technology is its ability to accelerate production. Also, the software algorithms resulted in reduced cycle times and minimised tool wear. These developments underscore a commitment to refining CNC programming in die and mould manufacturing. It monitors cutting tool performance and ensures precise control and efficient tool movement. This optimisation has led to a reduction in manufacturing processes, resulting in a continuous workflow. Each year brings fresh additions to the core software, continually boosting the efficiency of mould manufacturing. Consequently, the cycle from CAD design to actual production on the factory floor gets reduced, with improvement in overall accuracy.
The Indian die and mould industry is on the brink of significant improvements, as indicated by a TAGMA survey forecasting a growth rate of 10-15 percent in the coming years. A couple of Tools Rooms with foreign direct investment (FDI) have already set up shop in the country. To capitalise on this opportunity, existing toolmakers in India need more gearing up to embrace these new technologies to stay competitive. The technologies call for upgrading skills. In light of the need to train the workforce, Vivek Nanivadekar, Executive Director of FIBRO India Precision Products, underscores the importance of aligning the education system with industry needs. He advocates for a swift examination of the curriculum in technical institutes across India. These educational programs should be upgraded to include the latest innovations and techniques to ensure that graduating toolmakers are well-versed in the advancements of the field. This, in turn, enhances employability in factories where new technologies and machines are in use. The call for the right training and education in the Indian die and mould industry will be a course toward progress and competitiveness.
Way forward
Cutting-edge advancements in materials and design techniques mark the die and mould industry transforming. It results in enhanced efficiency, durability, and adaptability in manufacturing. A hybrid manufacturing approach that fuses Additive Manufacturing (AM) and Subtractive Manufacturing (SM) is taking centre stage, promising varied possibilities.
Talking about the growing importance of high-tech manufacturing in die and mould tool rooms, Vineet says that precision manufacturing – a hallmark of this industry, seamlessly caters to the exacting demands of the aerospace and defence sectors. CNC machines are at the forefront. They ensure alignment of every detail. Such machines meet stringent aerospace standards while tirelessly crafting intricate dies for complex vehicle components in the automotive sector.
Additive manufacturing and 3D printing technologies are revolutionising component production, offering rapid prototyping, reducing material waste, and enhancing design freedom. As industries adapt and innovate, the die and mould sector will play a decisive role in shaping the manufacturing landscape. Automotive remains a prime driver, and as the industry navigates changes, toolmakers will continue to play a vital role. The future holds the promise of IoT-enabled machines, the adoption of Industry 4.0 principles, and the digitisation of applications. The advancements must propel the industry to new technologies, refurbishing the industry’s future.
================================
Vineet Seth, Managing Director – South Asia & Middle East, Mastercam APAC.
“Manufacturers are now producing custom moulds explicitly tailored to the unique components required for EVs, such as battery casings and motor parts.”
Shatyabrata Das, Sr. General Manager, IAC-International Automotive Components
“With 3D printing, cooling channels can be designed and printed precisely to meet specifications, greatly enhancing cooling efficiency.”
Vivek Nanivadekar, Executive Director, FIBRO India Precision Products Pvt. Ltd.
“To align the education system with industry needs, a swift examination of the curriculum in technical institutes across India is needed.”
Maulik Patel, Executive Director, Sahajanand Laser Technology Ltd.
“Modern features of today’s laser cutting machines are compact and faster for more precise cutting speeds. These robust systems can cut various materials.”
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.


















 English
English Hindi
Hindi