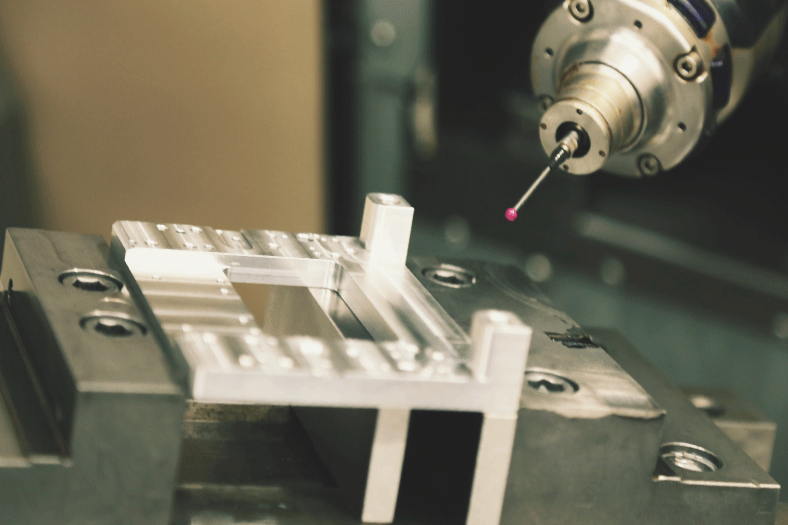
Milling to perfection
October 9, 2018 2:49 pm
Die and mould plays a pivotal role for most of the manufacturing industries. Here is an exclusive report on milling and its new innovative technologies
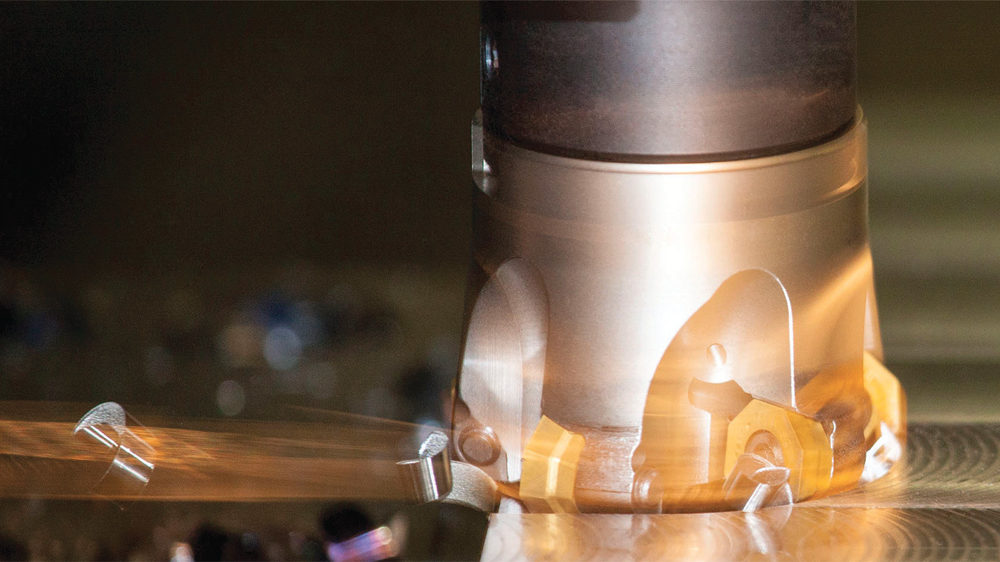
More than 2/3rd of metal cutting operations are estimated to be in the tool rotating applications, deploying milling and drilling families of tools. This milling percentage assumes an even more significant share in the aerospace industries, power sector, defence etc. apart from automotive industry.
Revolutionary movement in the milling technology
Milling forms the core metal cutting operations when it comes to manufacturing of prismatic components. This segment of manufacturing industry is growing rapidly.
Manufacturing of prismatic parts with close tolerances are increasingly seen in several industry sectors. From the point of view of power and machine tools, the trend is more and more towards minimising number of setups, and attempting to finish parts in single clamping by using multi-axis machines. Use of such machines and set up is seen more in newly emerging sectors such as aerospace and die and mould among others.
According to Naveen V Vastrad, Senior Manager – Marketing (Products), TaeguTec India, when it comes to cutting tools, customer expectations mostly centre around productivity and low cost per part. There are development taking place in multiple directions in this regard:
• Heavy mills: These tools use high depths of cut and moderate feed rates to achieve high metal removal rates and productivity. Generally, they are suitable for powerful heavy machines and large parts.
• High feed mills: Over the years, companies have adopted these types of tools that use low depths of cut, but exceptionally high feed rates to maximise metal removal rates. It is used in die and mould industries and several profile milling applications involving large metal removal. It is ideal on machines with moderate spindle power.
• Alternate materials: When it comes to productive and non-ferrous milling, there is a significantly heightened usage of milling cutters with PCD as cutting tools. Ceramics are also used in milling cast iron and Ni-based alloys. CBN is used in several areas requiring high flatness and surface roughness in cast iron milling.
• Multiple edges: There is also an effort in this direction of using shapes of inserts that enable as many as 14 to 16 cutting edges in face milling. This significantly reduces tooling cost per cutting edge.
New technologies
Exotic materials in components machining
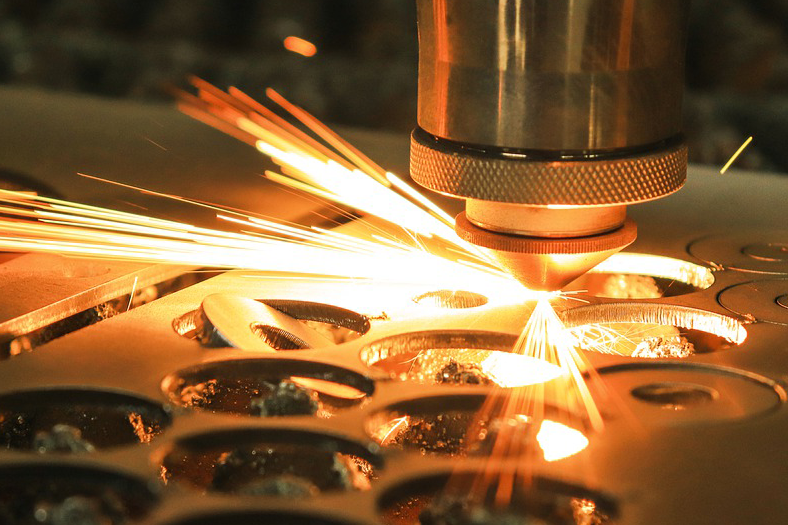
There is an all-round development taking place in the areas of drilling, milling, turning, parting and grooving, and tooling systems. Direction of development is to address the increasing use of difficult machine materials, higher accuracy requirements of parts, and low tool cost per component. Innovations are centred around shapes, geometries, carbide grades, coating and alternate materials.
Naveen says, “In the future, we can see an increased use of exotic materials in machining components, with high heat, wear resistance and difficult-to-machine characteristics: inconel, rene, titanium, duplex stainless steel, nickel, cobalt and titanium-based alloys.” They have been developed and applied in various industries such as power generation, aerospace, oil and gas, valves, pumps, etc. This has resulted in soaring demand for high productivity carbide grades with longer tool life to deal with the demanding machining conditions of difficult-to-cut materials. In these cases, conventional machining grades and geometries may not be useful.
“For such conditions and applications, TaeguTec has two new milling grades – TT3540 and TT9540 grades. These new PVD-coated and CVD-coated carbide grades with advanced substrate will offer optimal balance of improved toughness and wear resistance to customers for machine stainless steel, nickel, cobalt and titanium based alloys,” adds Naveen.
SiAlON ceramic grades
TaeguTec has also launched two new SiAlON ceramic grades – the TC3020 and TC3030 – that offer superior performance in high temperature alloy machining. Both TC3020 and TC3030 ceramic grades are suitable for high temperature alloy machining where difficult-to-cut materials such as inconel, rene and titanium are used. These ceramic grades are characterised by their excellent toughness and anti-chipping capabilities making them the best choice for both interrupted and continuous machining.
In terms of insert geometries, for instance, TaeguTec’s chip splitter inserts reduce cutting forces during heavy milling, while achieving high table feed without the vibrations and the noise. The insert’s helical cutting edge geometry enables double feed rates and improved chip evacuation with minimal heat generation. These chip splitter inserts are an economical option and development over the conventional and expensive vibration dampening cutters.
Dormer Pramet’s offers
Gautam Ahuja, Managing director, Dormer Pramet India says, “Dormer Pramet’s family of solid carbide milling cutters offers a variety of options from roughing through to finishing. The S2 assortment includes a range of neck options for deep milling and multi-flute designs to support numerous applications in tough steels, titanium and nickel.”
Its differential pitch cutters (S260, S262, S264), for example, reduce chatter and offer fewer tool offset adjustments, providing effective chip removal at high feed rates.
The trio of cutters – available in diameters from 3 mm-20 mm – feature an optimised cutting edge to reduce chipping and prolong tool life. All have an AlCrN coating for improved wear and oxidation resistance.
Gautam adds, “The S264 milling cutter has a robust corner chamfer on the end teeth to further reduce chipping and a roughing profile for greater removal rates.
Also, the S262’s corner radius provides a more precise finish and optimises performance, especially in ramping operations.
Meanwhile, Dormer Pramet’s six to eight-flute cutters (S225, S226, S227) feature a high helix angle to keep the cutting edges constantly engaged with the work-piece. This results in clean, efficient machining and a high-quality surface finish.
Several neck options are available to support pocket milling, up to 8.8xD, by preventing contact between the shank and work-piece, eliminating the risk of vibration and scouring.
Gautam further adds, “To support general milling applications, the company’s range of four-flute cutters (S216, S217, S218, S219) offer a reach up to 9xD. This range also features an optimised cutting-edge design and an AlTiN coating for high hot hardness and oxidation resistance. A special edge treatment provides a smooth and quiet machining process, further prolonging tool life.”
When it comes to productive,non-ferrous milling,there is significantly heightened usage of milling cutters with PCD as cutting tools.
Naveen V Vastrad,Senior Manager- Marketing(Products), TaeguTec India
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.
















 English
English Hindi
Hindi