Preventing the spread of COVID-19 through touch with anti-viral surface coating
April 13, 2020 5:19 pm
As declared by World Health Organization (WHO), presently the whole world is facing a pandemic and a global crisis caused by a novel virus that was discovered to be the cause of a large and rapidly spreading outbreak of respiratory disease, including potentially fatal pneumonia, in Wuhan, China (starting 9th January, 2020). The virus was provisionally designated 2019-nCoV and later given the official name SARS-CoV-2; the disease caused by the virus was officially named Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) by WHO.
SARS-CoV-2 is an enveloped, positive sense, single-stranded RNA virus. The coronavirus is so named because of its characteristic solar corona (crown-like) appearance when observed under an electron microscope. This appearance is produced by the peplomers of the surface (or spike; designated S) glycoprotein radiating from the virus lipidenvelope.The SARS-CoV virion is spherical with an average diameter of 78 nm.
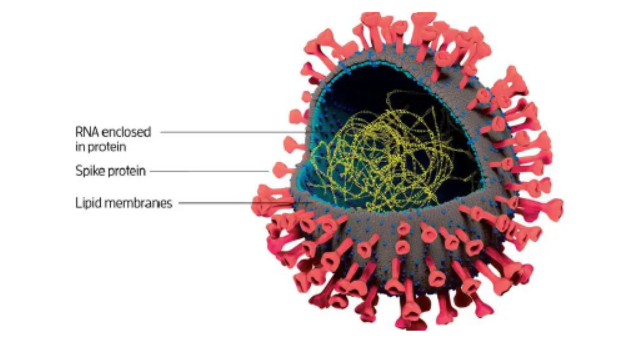
Figure 1: Anatomy of COVID-19 virus (Figure from New Scientist Journal)
SARS-CoV-2 is a delicate but highly contagious virus capable of spreading primarily from person to person around the world. It also spreads when an infected person coughs or sneezes and a droplet lands on a surface or object. When a person touches the surface that has the virus on it, and then touches his/her nose, mouth or eyes, he/she could pick it up. On the personal level, hygiene measures are recommended to prevent the spread of the disease, especially in institutions where individuals are in contact with patients or contaminated fomites. Washing hands with soap and water or with alcohol-based hand rubs is effective for interrupting virus transmission. Although viruses don’t grow on non-living surfaces, recent studies show that coronavirus can remain viable or infectious on metal, glass, wood, fabrics and plastic surfaces for several hours to days, irrespective of the surface looking dirty or clean. However, the coronavirus is relatively easy to destroy, and using simple disinfectants like ethanol (62-71 percent), hydrogen peroxide (0.5 percent) or sodium hypochlorite (0.1 percent) can break the delicate envelope that surrounds the tiny microbe. Nonetheless, it’s practically impossible to sanitise the surfaces all the time and it doesn’t guarantee that the surface won’t get contaminated again. It’s a much wiser solution in such a scenario if the surface can repel the pathogens, making it non-stick, and/or “sanitise by itself” by neutralising the contaminated pathogens quickly, thus eliminating the possibilities of transfer of microorganisms to the human body and its subsequent spread. A study shows that the spike glycoprotein of COVID-19 allows the virus to dock and bind to the ACE2 surface proteins of human epithelial cells in the respiratory track, thereby infecting these cells. Association of the COVID-19 spike glycoprotein with host ACE2 surface protein is a crucial step for infection.
Our research aim is to create a surface coating with relatively low surface energy value which may repel the spike glycoprotein to anchor the surfaces of landing, also use of active chemicals that could inactivate the spike glycoprotein as well as viral nucleotides. As we already have developed an anti-microbial coating solution virtually for all surfaces with effective combination of nano-actives, having proven literature support that it is anti-viral too, we are pretty convinced about its performance as an antiviral and it should resist the transmission of virus from non-living articles to living body cells through touch.
Literature survey shows that the nano-particles (NPs) of various metals and metal oxides like zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs), cuprous oxide nanoparticles (CuONPs), silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), nano sized copper (I) iodide particles (CuINPs), gold nanoparticles on silica nanoparticles (Au-SiO2NPs) and also some quaternary ammonium cations commonly called QUATs are very promising and well proven to inactivate the virus.
The product that we have developed as an antimicrobial coating for surfaces like fabrics, plastics, metals and concretes, NANOVA® HYGIENE+TM, contains the cocktails of non-migratory QUATs and positively charged AgNPs as bioactive nanoparticles and dispersing this into binder polymers. This anti-microbial coating also shows extremely low surface energy value (>20 mN/m) and behaves as an omniphobic surface by repelling water and oil together. Contact angels were >130o and >50o when measured against water and hexadecane as probes, respectively. This coating has proven test reports on protection against bacteria pathogens up to 99.9 percent as per the global standard JIS Z2801. The coated surfaces also have evidence to work effectively against fungi and algae pathogens.From the available published data in literatures, we can safely opine that NANOVA® HYGIENE+TM would be a potential coating candidate to repel and inactivate the virus on the surface, and hence could be a potential material to address the present problem of COVID-19 spread through surface touch.
The plausible ways of functioning of the doped nano actives materials against COVID-19 would be as follows:
- As AgNPs have been reported to inhibit the replication of virus nucleotides, its main mechanism is being virulent. It binds to electron donor groups such as sulphur, oxygen, and nitrogen commonly found in enzymes within the microbe. This causes the enzymes to be denatured, thus effectively incapacitating the energy source of the cell and making the microbe die quickly.
- The cationic silver (Ag+) or QUATs might work to inactivate the SARS-CoV-2 by interacting with its surface (spike) protein S based on its charge like it works in HIV, hepatitis, etc.
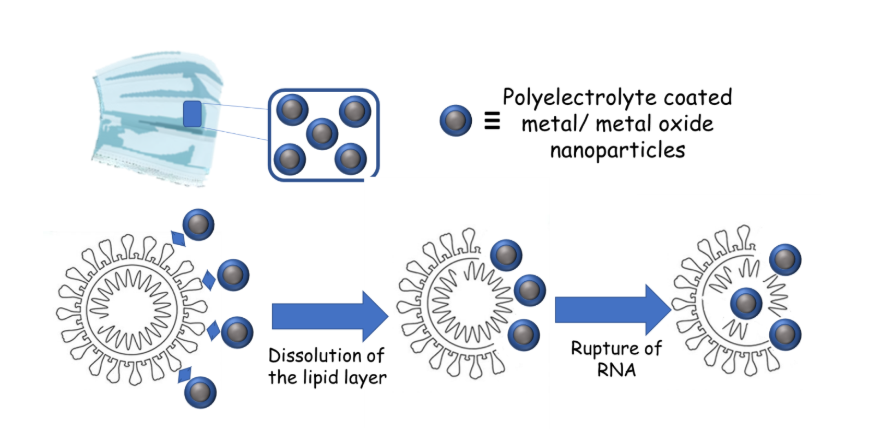 Figure 2: Schematic repetition of anti-viral coating with our nano-actives for inactivation of any adhered virus on the surfaces
Figure 2: Schematic repetition of anti-viral coating with our nano-actives for inactivation of any adhered virus on the surfaces
As our NANOVA® HYGIENE+TM omniphobic antimicrobial coating shows complete disablement of various pathogenic bacteria already and further on the basis of available scientific supports, we are of the opinion that the present formula should work against a broad spectrum of viruses as well. However, test and validation are being conducted on a war footing at South India Textile Research Association (SITRA), Coimbatore to establish its efficacy on inactivation of COVID-19 on different surfaces to stop the secondary spread from various surfaces to living cells through touch. Once found active, it has numerous applications virtually for all surfaces like fabric (mask, gloves, doctor coats, curtains, bed sheet), metal (lifts, doors handle, knobs, railings, public transport), wood (furniture, floors and partition panels), concrete (hospitals, clinics and isolation wards), plastics (switches, kitchen and home appliances) and potentially could save many lives.
For more information, contact:
Dr Swapan Kumar Ghosh, Director, Nova Surface-Care Centre Pvt. Ltd.
Unit Nos. D107 to D112, Kailash Industrial Complex
Vikhroli – Hiranandani Link Road, Vikhroli (W)
Mumbai 400 079, India.
(O)+91-22-61278175; (H/P) +91-9833237749
E-mail: swapan.ghosh@nsccindia.com
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.















 English
English Hindi
Hindi